In the quest for cleaner, healthier indoor air, many homeowners turn to air purifiers. Among various technologies, UV light air purifiers have gained significant attention, promising to neutralize airborne pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and mold spores. The appeal of effortlessly destroying invisible threats is strong, making UV-C air purifiers a popular choice. But as a discerning consumer, you might be asking: do air purifiers with UV light really work as effectively as advertised, or is it merely clever marketing? This comprehensive guide will delve into the science, efficacy, and potential risks associated with germicidal UV air purifiers, helping you understand if they are a valuable addition to your indoor air quality strategy or an unnecessary expense. We aim to separate scientific principle from marketing claims, providing you with the necessary context to make an informed decision about these ultraviolet air purification systems.
The Science Behind the Glow: How UV-C Light Targets Airborne Threats
Understanding the effectiveness of UV light air purifiers requires grasping the fundamental science behind ultraviolet (UV) light, specifically the UV-C spectrum, and its interaction with microorganisms. This isn't just about a 'special light' that zaps germs; it's about a precise photochemical process utilized in disinfection for over a century.

Understanding the Ultraviolet Spectrum: The Power of UV-C
Ultraviolet radiation is an invisible segment of the electromagnetic spectrum, categorized into three main bands:
- UV-A (315-400 nm): Common UV radiation, causes skin aging.
- UV-B (280-315 nm): More energetic, causes sunburn, linked to skin cancer.
- UV-C (100-280 nm): Shortest, most energetic. Natural UV-C is absorbed by the ozone layer. Artificially generated UV-C is used for its potent germicidal properties in air purification systems, with 253-265 nm being most effective for inactivation.
The Mechanism of Inactivation: Disrupting Life's Blueprint
The germicidal power of UV-C 광선 lies in its ability to photochemically alter the genetic material (DNA and RNA) of microorganisms. When exposed to sufficient UV-C photons, damaging bonds form within the DNA/RNA, disrupting the microbe's ability to reproduce. An organism that cannot reproduce is rendered non-infectious and harmless .
It's vital to distinguish this from "killing" or "removal." UV-C inactivates microbes; it doesn't physically destroy or remove them from the air. The inactivated microbe remains, but its capacity to cause disease is neutralized. This distinction is significant because inactivated pathogens can still trigger allergic responses. Thus, UV-C technology alone is an incomplete solution for comprehensive 실내 공기질 improvement.
Historical Context and Modern Applications
UV light as a disinfectant dates back over a century. UVGI has been trusted in hospitals, water treatment, and laboratories. This scientific credibility is leveraged by manufacturers of consumer 공기 청정기.
UV-C technology is used in HVAC systems and standalone air purification devices. While the principle is the same, effectiveness in small consumer devices faces challenges not present in professional systems. Marketing often oversimplifies the transition from established science to practical home application, leading to questions about whether these devices "really work" in a home environment.
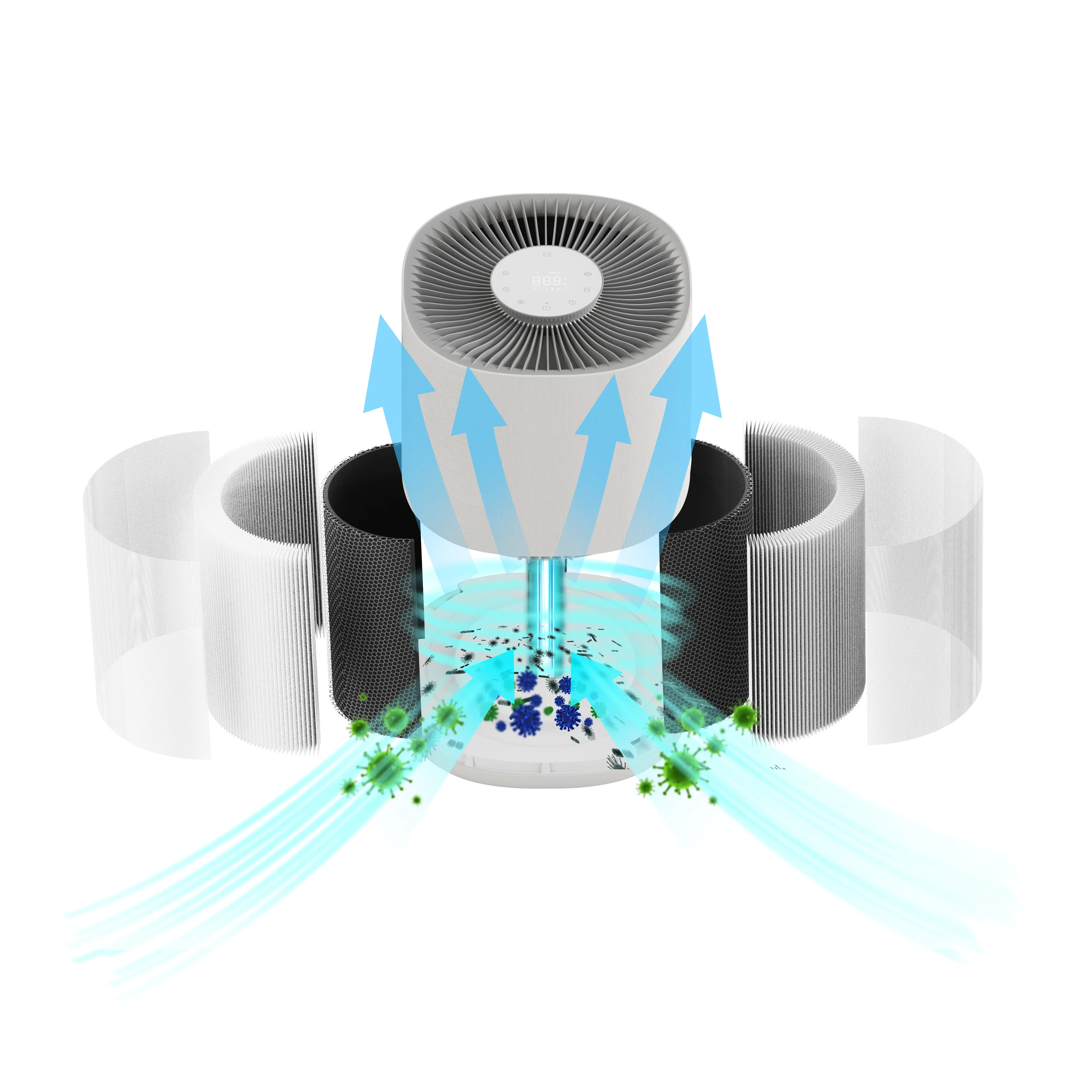
The Reality Check: Why Most UV Air Purifiers Fall Short for "On-the-Fly" Disinfection
While UV-C light can inactivate pathogens, its effectiveness in a consumer air purifier with UV light is complex. Real-world performance is a nuanced equation, and failure in any area can render the UV feature ineffective. This section reveals the gap between theoretical potential and actual performance of UV light air purification systems.
The Efficacy Equation: UV Dose – Intensity x Time
Effective UVGI relies on UV dose, the total UV-C energy delivered to a microorganism. Dose is calculated as Intensity (strength of light) x Time (duration of exposure).
- Intensity: Strength of UV-C light (µW/cm²), dependent on lamp power, design, age, and distance.
- Time: Duration of exposure, or "dwell time," in seconds.
Different microbes require specific doses (µW⋅s/cm²) for inactivation. Robust organisms like mold spores need higher doses. Therefore, a UV lamp is only meaningful if it can deliver the necessary dose within the system's operational constraints.
The Dwell Time Dilemma: Airflow vs. Exposure
The greatest challenge for UV-C technology in 공기 청정기 is achieving sufficient dwell time. Air purification requires high airflow (measured by CADR), but this means pathogens pass the UV lamp extremely quickly—often a fraction of a second. This fleeting exposure is usually too short for an inactivating dose, especially for resistant microbes. Many consumer units are ineffective for "on-the-fly" disinfection, despite marketing claims. Some designs attempt to increase dwell time, but their effectiveness in typical consumer models is often unverified.
Intensity and Proximity: The Inverse-Square Law in Action
Light intensity decreases dramatically with distance, governed by the inverse-square law . Pathogens further from the UV lamp receive significantly lower doses. In a turbulent airstream, it's statistically improbable that every microbe will pass close enough for a lethal dose. Effectiveness depends on lamp power, quality, and chamber geometry. A low-wattage or poorly positioned lamp has minimal impact.
Environmental and Operational Factors Affecting Performance
Several factors degrade UV-C system performance:
- Humidity and Temperature: High humidity (>60%) and cold temperatures reduce UV output of mercury vapor lamps.
- Lamp Maintenance and Degradation: UV-C lamps have a finite lifespan (6,000-10,000 hours). Intensity degrades over time. Unreplaced bulbs or dust/grime on the lamp severely impede performance.
- Biofilm Shielding: Microbes in respiratory fluids or on dust particles can be shielded from UV-C light, preventing inactivation.
Given these hurdles, the primary function of UV in most consumer devices is not real-time air disinfection. Instead, a UV lamp strategically positioned to irradiate a HEPA filter can sanitize its surface, preventing captured mold and bacteria from colonizing and multiplying. This is a useful function for system hygiene, but a more modest role than often advertised. The consumer market lacks a standardized "Germicidal Delivery Rate" metric, forcing reliance on marketing claims often based on idealized lab tests, not real-world performance.
While the efficacy of UV-C technology in consumer 공기 청정기 is debatable, potential risks are more concrete. Introducing high-energy radiation into an uncontrolled indoor environment can have consequences beyond direct UV exposure, including generating harmful indoor air pollutants. These unintended byproducts can negate benefits and make air more hazardous, raising questions about the overall safety of some ultraviolet air purification systems.
Direct UV-C Exposure: A Contained Hazard
UV-C radiation is harmful to skin and eyes. However, in competently designed 공기 청정기, the UV-C lamp is enclosed, preventing leakage. Interlock safety switches often shut off the lamp if the unit is opened. Risk to end-users is minimal; the primary hazard is to maintenance personnel who don't disconnect power.
The More Insidious Threat: Ozone Production and Secondary Pollutants
More concerning are potential harmful byproducts like ozone and VOCs.
Ozone Production: A Lung Irritant
Some UV lamps (especially older/lower-quality) produce ozone (O₃), a known lung irritant that worsens respiratory issues. It's marketed as a powerful oxidant, but it reacts with lung tissue, causing harm. California Air Resources Board (CARB) regulates against ozone-emitting 공기 청정기.
Creating New Pollutants: The Unintended Chemical Reaction
Alarmingly, even "ozone-free" UV air purifiers can create new harmful pollutants. UV-C 광선 can react with common household chemicals (VOCs) from cleaning products, furniture, etc., to produce dangerous secondary pollutants like:
- Formaldehyde: A known human carcinogen and respiratory irritant.
- Ultrafine Particles: Microscopic particles that penetrate deep into lungs, contributing to health problems.
This means a device intended to improve 실내 공기질 could worsen it by introducing toxic compounds. The chemical reactions are complex and depend on specific VOCs, but the potential for unintended consequences is significant.
Your Safety Shield: The UL 2998 "Zero Ozone" Certification
To ensure safety, look for the UL 2998 "Zero Ozone" certification. This UL standard verifies an 공기 청정기 does not produce ozone above CARB limits.
Insisting on UL 2998 certification is non-negotiable for any electronic air cleaner, including those with 자외선. Without it, ozone emissions are unverified, posing a health risk. This certification also implies testing for other harmful byproducts, making it a reliable indicator of a safer product. Always check for this label when considering a UV 공기 청정기 or any 공기 정화 시스템 that uses electronic components.

The Winning Strategy: Building Your Air Purification A-Team for Optimal Indoor Air Quality
Given the limitations of UV light air purifiers for "on-the-fly" disinfection, relying solely on UV-C technology is insufficient. The most effective strategy for truly clean indoor air is a multi-stage approach, leveraging different 공기 정화 기술.
The Undisputed Champions: HEPA and Activated Carbon Filters
Before any supplemental technologies like 자외선, the foundation of any effective 공기 정화 시스템 must be high-quality mechanical filtration:
- HEPA Filter (High-Efficiency Particulate Air): Captures 99.97% of airborne particles 0.3 microns, including dust, pollen, pet dander, mold spores, and many bacteria/viruses. HEPA filtration physically traps pollutants, removing them from breathing air. Prioritize a True HEPA filter.
- Activated Carbon Filter: Ineffective against particulates, but excels at adsorbing gases, odors, and VOCs from cleaning products, paints, etc.. Essential for comprehensive 실내 공기질.
The "UV vs. HEPA" Myth: A Collaborative Approach
It shouldn't be 자외선 vs. HEPA 필터. Effective air purification systems use a multi-stage approach. A 자외선 component is most plausibly beneficial for sanitizing the HEPA filter surface, preventing growth of captured biological contaminants. It's a secondary line of defense for filter hygiene, not primary air disinfection.
Bottom line: A purifier with a high-quality 진정한 HEPA 필터 and a substantial 활성탄 필터 is the essential foundation. A 자외선 is, at best, a supplemental feature for system hygiene and additional protection against certain biological contaminants, never the primary reason for purchase.
The Future of Air Disinfection: A Glimpse at Far-UVC Technology
While traditional UV-C 광선 in consumer 공기 청정기 has limitations, Far-UVC technology is an evolving field. Unlike conventional germicidal UV-C (which damages skin/eyes), Far-UVC (207-222 nm) can inactivate airborne viruses/bacteria without penetrating human skin/eyes. This could allow safe, continuous disinfection in occupied spaces.
However, Far-UVC technology is still emerging, not widely available in consumer 공기 청정기, and undergoing long-term safety/efficacy studies. It's an exciting future for air disinfection, but not a feature to rely on in current home air purification systems.

Conclusion: Your Smart Shopper's Checklist for Air Purifiers with UV Light
So, do air purifiers with UV light really work? The answer is nuanced, depending on your expectations. While UV-C light's germicidal science is sound, its application in many consumer-grade air purification systems is often limited by practical constraints and can introduce risks. Here's your smart shopper's checklist to navigate the world of UV air purifiers and ensure you're investing in truly effective 실내 공기질 solutions:
- Does UV light alone clean the air? No. It inactivates microorganisms but doesn't remove particulate matter or gaseous pollutants.
- Is it effective for killing airborne germs as they fly past? Unlikely, due to insufficient dwell time.
- Does it help keep the filter clean? Yes, this is the most plausible benefit of a UV-C component.
- Does it come with risks? Yes, potential for ozone and harmful secondary pollutants.
Your Actionable Buying Guide for Optimal Air Purification:
- Prioritize Filtration: The absolute foundation of effective 공기 정화 is mechanical filtration. Look for a unit with a 진정한 HEPA 필터 to capture particles and a substantial 활성탄 필터 to adsorb gases and odors. These are non-negotiable for comprehensive clean air.
- Check the CADR: Ensure the Clean Air Delivery Rate (CADR) is appropriate for your room size. A higher CADR means quicker, more effective air cleaning.
- Demand Safety: Insist on UL 2998 Certification. This is paramount for any electronic air cleaner, including those with 자외선. It verifies the device doesn't produce harmful ozone and has been tested for other byproducts.
- Evaluate UV Critically: View the UV feature as a secondary "bonus" for system hygiene (preventing mold/bacteria growth on the filter), not the main selling point for airborne germ destruction. If a UV 공기 청정기 is your choice, ensure it meets safety standards.
- Consider the True Cost: Factor in the price and lifespan of replacement filters 그리고 의 UV bulb. UV bulbs degrade and need regular replacement to maintain efficacy.
By understanding the science, recognizing limitations, and prioritizing safety certifications, you can make an informed decision about 자외선이 있는 공기 청정기 and breathe easier knowing you've chosen the best solution for your home's 실내 공기질.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about UV Light Air Purifiers
Q1: What is UV-C light and how does it work in an air purifier?
A1: UV-C light is a specific type of ultraviolet radiation with germicidal properties. In an 공기 청정기, it damages the DNA/RNA of microorganisms (like bacteria, viruses, and mold spores) as they pass, rendering them inactive. It does not physically remove them.
Q2: Are UV air purifiers effective at killing airborne viruses and bacteria?
A2: While UV-C can inactivate pathogens, its effectiveness in consumer 공기 청정기 for "on-the-fly" airborne disinfection is often limited due to insufficient dwell time. Their primary benefit is often filter sanitization.
Q3: Do UV air purifiers produce ozone?
A3: Some UV lamps can produce ozone, a lung irritant. Look for UL 2998 "Zero Ozone" certified 공기 청정기 to ensure no harmful ozone emissions.
Q4: What are the potential risks of using a UV air purifier?
A4: Risks include ozone production and creation of harmful secondary pollutants (formaldehyde, ultrafine particles) from reactions with household chemicals. Direct UV-C exposure is harmful, but mitigated in enclosed units.
Q5: What should I look for in an effective air purifier?
A5: Prioritize a 진정한 HEPA 필터 for particles and a substantial 활성탄 필터 for gases/odors. Check CADR for room size. If considering UV, ensure UL 2998 "Zero Ozone" certified and view it as a supplemental benefit for filter hygiene.






